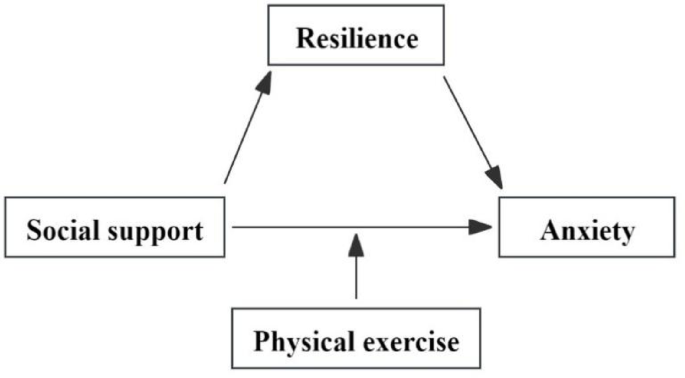
Social support and anxiety, a moderated mediating model
Barlow, D. H. Unraveling the mysteries of anxiety and its disorders from the perspective of emotion theory. Am. Psychol. 55 (11), 1247–1263. (2000).
Google Scholar
Hartley, C. A. & Phelps, E. A. Anxiety and Decision-Making. Biol. Psychiatry. 72 (2), 113–118. (2012).
Google Scholar
Javaid, S. F. et al. Epidemiology of anxiety disorders: global burden and sociodemographic associations. Middle East. Curr. Psychiatry. 30 (1), 44. (2023).
Google Scholar
Tan, G. X. D. et al. Prevalence of anxiety in college and university students: an umbrella review. J. Affect. Disorders Rep. 14, 100658. (2023).
Google Scholar
Perlis, R. H. et al. Irritability is associated with anxiety and greater severity, but not bipolar spectrum features, in major depressive disorder. Acta Psychiatry. Scand. 119 (4), 282–289. (2009).
Google Scholar
Smoller, J. W. et al. The human ortholog of Acid-Sensing ion channel gene ASIC1a is associated with panic disorder and amygdala structure and function. Biol. Psychiatry. 76 (11), 902–910. (2014).
Google Scholar
Chellappa, S. L. & Aeschbach, D. Sleep and anxiety: from mechanisms to interventions. Sleep. Med. Rev. 61, 101583. (2022).
Google Scholar
Singh, I. & Jha, A. K. Anxiety, optimism and academic achievement among students of private medical and engineering colleges: A comparative study. J. Educational Dev. Psychol. 3, 222. (2013).
Google Scholar
Yang, X., Yang, C., Chen, P., Sun, X. & Wang, Y. Relationship among self-regulatory focus with depression,anxiety symptoms and suicidal risks. Chin. J. School Health, 41(09), 1354–1357. https://doi.org/10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2020.09.020
Gignac, G. E. & Szodorai, E. T. Effect size guidelines for individual differences researchers. Pers. Indiv. Differ. 102, 74–78. (2016).
Google Scholar
Sheehy, T. L., McDonough, M. H. & Zauber, S. E. Social comparisons, social support, and Self-Perceptions in group exercise for people with parkinson’s disease. J. Appl. SPORT Psychol. 29 (3), 285–303. (2017).
Google Scholar
An, X. M., RESEARCH ON THE ANXIETY & RELIEF OF COLLEGE STUDENTS BY MUSIC THERAPY. PSYCHIATRIA DANUBINA, 34: S934–S938. (2022).
Zhang, Y., A STUDY ON MITIGATION STRATEGIES OF PSYCHOLOGICAL & ANXIETY OF COLLEGE STUDENTS UNDER LEARNING STRESS. PSYCHIATRIA DANUBINA, 33: S699–S704. (2021).
Yu, Y., RESEARCH ON THE EFFECT OF ART EDUCATION AND ART DESIGN ON ALLEVIATING & COLLEGE STUDENTS’ PSYCHOLOGICAL ANXIETY FROM THE PERSPECTIVE OF PSYCHOLOGY. PSYCHIATRIA DANUBINA, 34: S1085–S1090. (2022).
Estrella-Proaño, A. et al. Anxiety and depression in first-year university students: the role of family and social support. Front. Psychol. 15, 1462948. (2024).
Google Scholar
Laksmiwati, E., Tondok, M. & Support, P. S. Academic Self-Efficacy, and Anxiety among Final Year Undergraduate Students: A Mediation Analysis. Bulletin of Counseling and Psychotherapy, 2023. 5: pp. 173–182. https://doi.org/10.51214/00202305514000
Thoits, P. A. Mechanisms linking social ties and support to physical and mental health. J. Health Soc. Behav. 52 (2). (2011). 145 – 61.
Huang, L., Qian, J. & Wei, H. A study of the correlation between coping styles, social support and psychosomatic symptoms in cancer patients. Chin. Mental Health J. 04 160–161 (1996).
Cohen, S. & Wills, T. A. Stress, social support, and the buffering hypothesis. Psychol. Bull. 98 (2). (1985). 310 – 57.
Barrera, M., Fleming, C. F. & Khan, F. S. The role of emotional social support in the psychological adjustment of siblings of children with cancer. Child. Care Health Dev. 30 (2). (2004). 103 – 11.
Miao, H. Y. et al. The protective influence of family support on anxiety, depressive symptoms, and suicidal ideation among elderly Chinese nursing home residents: A study of serial mediation. MEDICINE 103 (4). (2024).
Whittle, I. R. & Lim, J. X. Overcoming fear and anxiety during awake resection of brain tumours: family support can be pivotal to a successful outcome. Br. J. Neurosurg. 27 (1), 117–118. (2013).
Google Scholar
Pickering, L., Hadwin, J. A. & Kovshoff, H. The role of peers in the development of social anxiety in adolescent girls: A systematic review. Adolesc. Res. Rev. 5 (4), 341–362. (2020).
Google Scholar
La Greca, A. M. & Lopez, N. Social anxiety among adolescents: linkages with peer relations and friendships. J. Abnorm. Child. Psychol. 26 (2), 83–94. (1998).
Google Scholar
De Wit, D. J. et al. Perceptions of declining classmate and teacher support following the transition to high school: potential correlates of increasing student mental health difficulties. Psychol. Sch. 48 (6), 556–572. (2011).
Google Scholar
Boyd, C. P. et al. Eco-anxiety among Regional Australian Youth with Mental Health Problems: A Qualitative Study (EARLY INTERVENTION IN PSYCHIATRY, 2024). https://doi.org/10.1111/eip.13549
Meng, N., COVID-19-Related Factors. & et al in The Association between the Need for Psychological and Information Support from School and Anxiety and Depression. 27 (eds Sociodemographic, B.) (MEDICAL SCIENCE MONITOR, 2021). https://doi.org/10.12659/MSM.929280
Thapaliya, B. et al. Cross-continental environmental and genome-wide association study on children and adolescent anxiety and depression. Front. Psychiatry. 15. (2024).
Engel, G. L. The need for a new medical model: a challenge for biomedicine. Science 196 (4286). (1977). 129 – 36.
Deci, E. L. & Ryan, R. M. Intrinsic motivation and Self-Determination In human behavior. In perspectives In social psychology. (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4899-2271-7
Penedo, F. J. & Dahn, J. R. Exercise and well-being: a review of mental and physical health benefits associated with physical activity. Curr. Opin. Psychiatry. 18 (2), 189–193. (2005).
Google Scholar
Chen, C. et al. The exercise-glucocorticoid paradox: how exercise is beneficial to cognition, mood, and the brain while increasing glucocorticoid levels. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 44, 83–102. (2017).
Google Scholar
Rea, I. M. Towards ageing well: use it or lose it: exercise, epigenetics and cognition. Biogerontology 18 (4), 679–691. (2017).
Google Scholar
Ferioli, M. et al. Role of physical exercise in the regulation of epigenetic mechanisms in inflammation, cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, and aging process. J. Cell. Physiol. 234 (9), 14852–14864. (2019).
Google Scholar
Eöry, A. et al. Physical exercise as a resilience factor to mitigate COVID-Related allostatic overload. Psychother. Psychosom. 90 (3), 200–206. (2021).
Google Scholar
Çiçek, I. et al. Problematic social media use, satisfaction with life, and levels of depressive symptoms in university students during the COVID-19 pandemic: mediation role of social support. Psihologija 57, 177–197. (2024).
Google Scholar
Hu, Q. The effect of increased intensity of physical exercises on mental health andresilience among college students. Chin. J. School Health, 40(01), 83–85. https://doi.org/10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2019.01.022
Liu, Y. G. et al. The relationship between test anxiety and emotion regulation: the mediating effect of psychological resilience. Ann. Gen. Psychiatry. 20 (1). (2021).
Sun, Y. B. et al. The mediating effect of psychological resilience between social support and anxiety/depression in people living with HIV/AIDS-a study from China. BMC PUBLIC. HEALTH. 23 (1). (2023).
Zhu, D. X. et al. Inconsistency in psychological resilience and social support with mental health in early adolescents: A multilevel response surface analysis approach. J. Affect. Disord. 361, 627–636. (2024).
Google Scholar
Wang, Y., Bao, S. & Chen, Y. B. How does social media use influence the mental health of pancreatic cancer patients: a chain mediating effect of online social support and psychological resilience. Front. PUBLIC. HEALTH. 11. (2023).
Wu, X. L., Tang, L. & Gong, J. Correlation analysis of mental toughness, family social support, and anxiety of nursing staff. Am. J. TRANSLATIONAL Res. 16 (6), 2563–2570. (2024).
Google Scholar
Connor, K. M. & Davidson, J. R. Development of a new resilience scale: the Connor-Davidson resilience scale (CD-RISC). Depress. Anxiety. 18 (2), 76–82. (2003).
Google Scholar
Li, H. & Zhang, W. Review of psychological resilience research. J. Shandong Normal University(Social Sci.), 149–152. https://doi.org/10.16456/j.cnki.1001-5973.2006.03.029
Martin, A. J. et al. Academic buoyancy and psychological risk: exploring reciprocal relationships. Learn. Individual Differences. 27, 128–133. (2013).
Google Scholar
Wang, Y. & Chen, X. Stress and alcohol use in rural Chinese residents: A moderated mediation model examining the roles of resilience and negative emotions. Drug Alcohol Depend. 155, 76–82. (2015).
Google Scholar
Çiçek, M. Y. 0., fear of COVID-19 and smartphone addiction among Turkish adolescents: mitigating role of resilience. Family J. (2022).
Google Scholar
Lü, Y. et al. Effect of resilience and expression suppression on the relationshipbetween social support and posttraumatic growth among Front-lineMedical workers in the epidemic situation of COVlD-19. Chin. J. Clin. Psychol., 28(04), 743–746. https://doi.org/10.16128/j.cnki.1005-3611.2020.04.019
Lin, G. et al. Study on the correlation between perceived social support andpsychological resilience of paramedics in resisting COVlD-2019 pandemic. China Med. Equip., 17(05), 209–211. https://doi.org/10.3969/J.ISSN.1672-8270.2020.05.047
Çiçek, I. Effect of hope on resilience in adolescents: social support and social connectedness as mediators. 5: pp. 136–147. (2021). https://doi.org/10.47602/jpsp.v5i2.283
Green, Z., Çiçek, I. & Yıldırım, M. The relationship between social support and uncertainty of COVID-19: the mediating roles of resilience and academic Self-Efficacy. Psihologija 57, 407–427. (2024).
Google Scholar
Fang, D. et al. School bullying victimization-associated anxiety in Chinese children and adolescents: the mediation of resilience. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry Mental Health. 16 (1). (2022).
Jang, M. H. et al. Factors influencing resilience of burn patients in South Korea. J. Nurs. Scholarsh. 49 (5), 478–486. (2017).
Google Scholar
Kim, M. & Sok, S. Factors Influencing Resilience among Breast Cancer Survivors: Implications for evidence-based Practice21p. 87–95 (WORLDVIEWS ON EVIDENCE-BASED NURSING, 2024). 1https://doi.org/10.1111/wvn.12678
Agarwal, B., Brooks, S. K. & Greenberg, N. The Role of Peer Support in Managing Occupational Stress: A Qualitative Study of the Sustaining Resilience at Work Intervention68p. 57–64 (WORKPLACE HEALTH & SAFETY, 2020). 2https://doi.org/10.1177/2165079919873934
Aizpurua-Perez, I. et al. A randomized controlled trial of the effectiveness of a one-to-one peer support intervention on resilience, social support, and salivary cortisol in recently diagnosed women with breast cancer. Eur. J. Oncol. Nurs. 71. (2024).
Pointon-Haas, J. et al. A systematic review of peer support interventions for student mental health and well-being in higher education. BJPSYCH OPEN. 10 (1). (2023).
Gildner, T. E. et al. Associations between postpartum depression and assistance with household tasks and childcare during the COVID-19 pandemic: evidence from American mothers. BMC PREGNANCY CHILDBIRTH. 21 (1). (2021).
Matsumoto, R. et al. Impact of the Japanese Government’s ‘General Principles of Suicide Prevention Policy’ on youth suicide from 2007 to 2022. BJPSYCH OPEN. 10 (1). (2023).
Zazzarino, A., Reilly, A., Clay, Z. & JOURNAL OF PSYCHOSOCIAL NURSING AND MENTAL HEALTH SERVICES. Increasing psychiatric rehabilitation knowledge in a supported housing setting Pre- and posttest analysis., 57(6): pp. 39–44. (2019). https://doi.org/10.3928/02793695-20181219-01
Chen, J. et al. Family resilience and psychological resilience in cancer patients:chainmediating effect of perceived social support and meaning in life. Chin. J. Clin. Psychol., 27(06), 1205–1209. https://doi.org/10.16128/j.cnki.1005-3611.2019.06.026
Roohafza, H. et al. What’s the role of perceived social support and coping styles in depression and anxiety? J. Res. Med. Sci. : Official J. Isfahan Univ. Med. Sci. 19, 944–949 (2014).
Abdullah, S. et al. The relationship between stress and social support among flood victims. Procedia – Social Behav. Sci. 192, 59–64. (2015).
Google Scholar
McCrossin, J. & Lach, L. Parent-to-parent support for childhood neurodisability: A qualitative analysis and proposed model of peer support and family resilience. CHILD. CARE HEALTH Dev. 49 (3), 544–554. (2023).
Google Scholar
Şanli, M. E. et al. Positive childhood experiences as predictors of anxiety and depression in a large sample from Turkey. Acta. Psychol. 243, 104170. (2024).
Google Scholar
Rayani, S., Rayani, M. & Najafi-Sharjabad, F. Correlation between Anxiety and Resilience of Healthcare Workers during COVID-19 Pandemic in the Southwest of Iran29p. 21528–21536 (ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE AND POLLUTION RESEARCH, 2022). 15https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17284-x
Wu, M. et al. The relationship between uncertainty and acute procedure anxiety among surgical patients in Chinese mainland: the mediating role of resilience. BMC PSYCHIATRY. 23 (1). (2023).
Rayatpisheh, F. et al. Relationship between resilience and death anxiety of the older adults during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. BMC Geriatr. 23 (1). (2023).
Gabrovec, B., RESEARCH AND PUBLIC HEALTH. & et al Perceived Satisfaction with Online Study during COVID-19 Lockdown Correlates Positively with Resilience and Negatively with Anxiety, Depression, and Stress among Slovenian Postsecondary Students19 (INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENVIRONMENTAL, 2022). 12https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19127024
Devi, H. M., Purborini, N. & Chang, H. J. Mediating effect of resilience on association among stress, depression, and anxiety in Indonesian nursing students. J. Prof. Nurs. 37 (4), 706–713. (2021).
Google Scholar
Suroedova, E., Uvarova, G. & Shevkieva, N. Psychological structure of personal resources of coping behavior of high school students. E3S Web of Conferences, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/202125807090
Qu, N. & Li, K. Study on the reliability and validity of international physical activity questionnaire. Chin. J. Epidemiol. 25(3), 265–268 (2004).
Fan, M., Lü, J. & He, P. Chinese guidelines for data processing and analysis concerning the international physical activity questionnaire. Chin. J. Epidemiol., 35(8), 961–964. https://doi.org/10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2014.08.019
Spitzer, R. L. et al. A brief measure for assessing generalized anxiety disorder: the GAD-7. Arch. Intern. Med. 166 (10), 1092–1097. (2006).
Google Scholar
Schalet, B. D. et al. Establishing a common metric for self-reported anxiety: linking the MASQ, PANAS, and GAD-7 to PROMIS anxiety. J. Anxiety Disord. 28 (1), 88–96. (2014).
Google Scholar
Podsakoff, P. M. et al. Common method biases in behavioral research: a critical review of the literature and recommended remedies. J. Appl. Psychol. 88 (5), 879–903. (2003).
Google Scholar
Hayes, A. F. Partial, conditional, and moderated moderated mediation: quantification, inference, and interpretation. Communication Monogr. 85 (1), 4–40. (2018).
Google Scholar
Jiang, H. The Research about the Relationship between Socialsupport and Psychological help-seekingP. 45 (Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2007).
Xiao, H. et al. The effects of social support on sleep quality of medical staff treating patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in January and February 2020 in China. Med. Sci. Monit. 26, e923549. (2020).
Google Scholar
Hendryx, M., Green, C. A. & Perrin, N. A. Social support, activities, and recovery from serious mental illness: STARS study findings. J. Behav. Health Serv. Res. 36 (3), 320–329. (2009).
Google Scholar
Bowen, M. Family Therapy in Clinical Practice. New York (Aronson) 1978. (1978).
Carver, C. S., Scheier, M. F. & Weintraub, J. K. Assessing coping strategies: a theoretically based approach. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 56 (2). (1989). 267 – 83.
Pei, R. et al. A neural signature of social support mitigates negative emotion. Sci. Rep. 13 (1). (2023).
Ozbay, F. et al. Social support and resilience to stress across the life span: a neurobiologic framework. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 10 (4), 304–310. (2008).
Google Scholar
Mendonça, G. et al. Physical activity and social support in adolescents: a systematic review. Health Educ. Res. 29 (5). (2014). 822 – 39.
Liu, Y., Xiao, T., Zhang, W., Xu, L. & And Zhang, T. The Relationship Between Physical Activity and Internet Addiction Among Adolescents in Western China: A Chain Mediating Model of Anxiety and Inhibitory Control. Psychology, Health & Medicine 29, 1602–1618 (2024).
Sciolino, N. R. et al. Galanin mediates features of neural and behavioral stress resilience afforded by exercise. NEUROPHARMACOLOGY 89, 255–264. (2015).
Google Scholar
Liu, Y. et al. Relationship between bullying behaviors and physical activity in children and adolescents: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Aggress. Violent. Beh. 78, 101976. (2024).
Google Scholar
Sampedro-Piquero, P. & Moreno-Fernández, R. D. Building resilience with aerobic exercise: role of FKBP5. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 19 (8), 1156–1160. (2021).
Google Scholar
Orwin, A. Treatment of a situational Phobia-A case for running. Br. J. Psychiatry. 125, 95–98. (1974).
Google Scholar
Muller, B. & Armstrong, H. E. A further note on the running treatment for anxiety. Psychotherapy 12, 385–387. (1975).
Google Scholar
Silverman, M. N. & Deuster, P. A. Biological mechanisms underlying the role of physical fitness in health and resilience. Interface Focus. 4 (5), 20140040. (2014).
Google Scholar
Wang, Y. et al. Correlation between resilience and social support in elderly ischemic stroke patients. WORLD Neurosurg. 184 (2024). p. E518-E523.
de Andrade, B. G. et al. Social support and resilience: a look at adolescent motherhood. ACTA PAULISTA DE ENFERMAGEM. 35 (2022).
Costa, A. et al. Social support is a predictor of lower stress and higher quality of life and resilience in Brazilian patients with colorectal cancer. Cancer Nurs. 40 (5), 352–360. (2017).
Google Scholar
Kutcher, A. M., Byon, H. & Esquivel, J. H. Depression, anxiety, and resilience. J. Cardiovasc. Nurs. 39 (3). (2024). p. E72-E79.
Gong, Y. et al. Relationship between social support and anxiety among urban empty nesters: the mediating roleof psychological resilience. Chin. J. Gerontol., 43(20), 5109–5112. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2023.20.066
Katajavuori, N., Vehkalahti, K. & Asikainen, H. Promoting university students’ well-being and studying with an acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT)-based intervention. Curr. Psychol. 42 (6), 4900–4912 (2023).
Moè, A. Does the weekly practice of recalling and elaborating episodes Raise Well-Being in university students?? J. Happiness Stud. 23 (7), 3389–3406 (2022).
Google Scholar
Liu, Y. et al. The Relationship Between Family Support and Internet Addiction Among Adolescents in Western China: The Chain Mediating Effect of Physical Exercise and Depression. Bmc Pediatr. 25, 397 (2025).
Liu, Y. et al. The Mediating Role of Inhibitory Control and the Moderating Role of Family Support Between Anxiety and Internet Addiction in Chinese Adolescents. Arch. Psychiatr. Nurs. (2024).
Liu Y, Peng J, Ding J, et al. Anxiety mediated the relationship between bullying victimization and internet addiction in adolescents, and family support moderated the relationship. BMC Pediatr. 25(1), 8 (2025).
Liu, Y. et al. Anxiety, Inhibitory Control, Physical Activity, and Internet Addiction in Chinese Adolescents: A Moderated Mediation Model. Bmc Pediatr. 24, 663 (2024).
Xiao T, Pan M, Xiao X, Liu Y. The relationship between physical activity and sleep disorders in adolescents: a chain-mediated model of anxiety and mobile phone dependence. BMC Psychol. 12(1), 751 (2024).
Peng J, Liu Y, Wang X, Yi Z, Xu L, Zhang F. Physical and emotional abuse with internet addiction and anxiety as a mediator and physical activity as a moderator. Sci Rep. 15(1), 2305 (2025).
Liu, Y. et al. The Chain Mediating Effect of Anxiety and Inhibitory Control and the Moderating Effect of Physical Activity Between Bullying Victimization and Internet Addiction in Chinese Adolescents. The Journal of Genetic Psychology. 1–16.
Gan, Y. et al. A Chain Mediation Model of Physical Exercise and Brainrot Behavior Among Adolescents. Sci. Rep. 15, 17830 (2025).
Liu, Y. et al. The Mediating Effect of Internet Addiction and the Moderating Effect of Physical Activity On the Relationship Between Alexithymia and Depression. Sci. Rep. 14, 9781 (2024).
Liu, Y. et al. Physical Activity Moderated the Mediating Effect of Self-Control Between Bullying Victimization and Mobile Phone Addiction Among College Students. Sci. Rep. 14, 20855 (2024).
Luo, X. et al. Gender Mediates the Mediating Effect of Psychological Capital Between Physical Activity and Depressive Symptoms Among Adolescents. Sci. Rep. 15, 10868 (2025).
Yi, Z., Wei, L., Xu, L., Pang, W. & Liu, Y. Chain-Mediation Effect of Cognitive Flexibility and Depression On the Relationship Between Physical Activity and Insomnia in Adolescents. Bmc Psychol. 13, 587 (2025).
Wang, W., Wang, J., Liu, Y. & Deng, L. Exploring the Relationship Between Physical Activity and Social Media Addiction Among Adolescents through a Moderated Mediation Model. Sci. Rep. 15, 22209 (2025).
Jia, W. et al. Physical Exercise Moderates the Mediating Effect of Depression Between Physical and Psychological Abuse in Childhood and Social Network Addiction in College Students. Sci. Rep. 15, 17869 (2025).
Wang, J. et al. Physical Activity Moderates the Mediating Role of Depression Between Experiential Avoidance and Internet Addiction. Sci. Rep. 15, 20704 (2025).
Peng, J. et al. Mobile Phone Addiction was the Mediator and Physical Activity was the Moderator Between Bullying Victimization and Sleep Quality. Bmc Public Health. 25, 1577 (2025).
Zimet, G. D., Dahlem, N. W., Zimet, S. G. & Farley, G. K. The Multidimensional Scale of Perceived Social Support. J. Pers. Assess. 52, 30–41 (1988).
Yu, X. et al. Factor Structure and Psychometric Properties of the Connor-Davidson Resilience Scale Among Chinese Adolescents. Compr.Psychiatry. 52, 218–224 (2011).
link






