Laryngitis Symptoms, Causes & Treatment
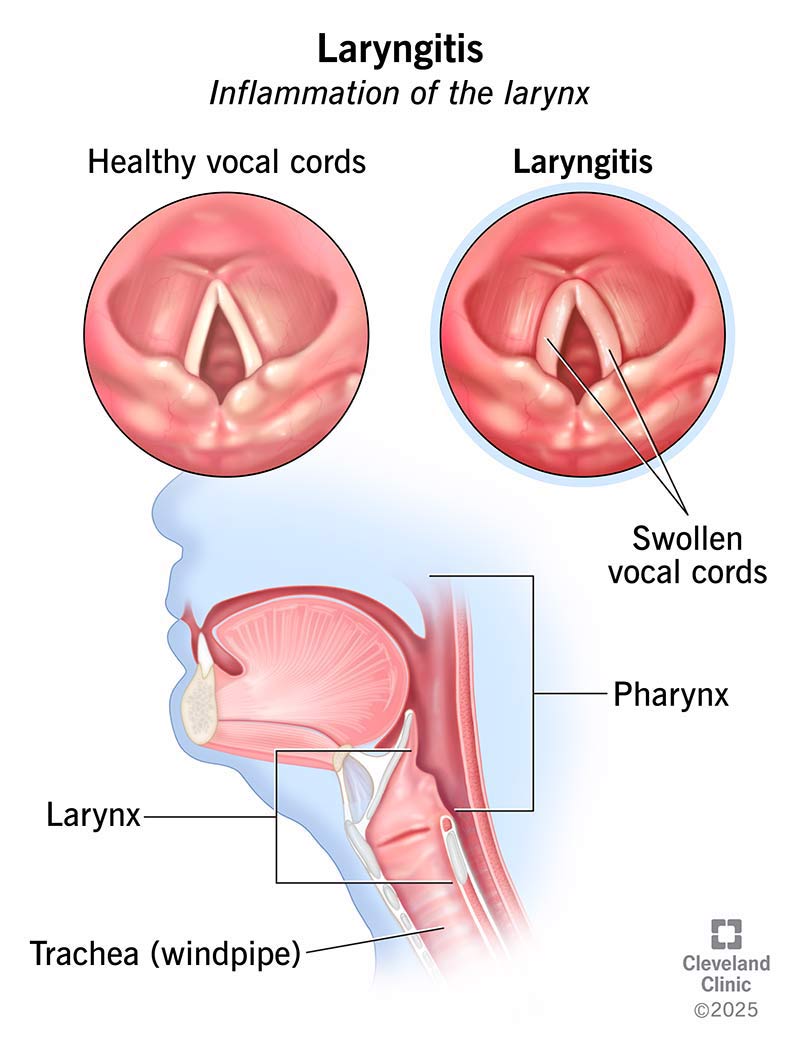
Symptoms of laryngitis
Some of the most common laryngitis symptoms include:
- Barking-like cough or dry cough
- Feeling like you’ve got a lump in your throat or feeling like you need to keep clearing your throat
- Hoarseness or a weak voice (dysphonia)
- Losing your voice
- Pain while using your voice
- Tickling or rawness in your throat
For the acute form of laryngitis, the symptoms are short-lived and last between three and seven days. If the symptoms last more than three weeks, that’s known as chronic laryngitis. The chronic form of this condition is most likely to cause a barking-like cough or globus sensation.
When laryngitis happens with certain symptoms, it might affect your ability to breathe, making it a bigger concern. If you have these dangerous symptoms, call your healthcare provider for an appointment. If your child has them, call their pediatrician or take them to get medical attention. The dangerous symptoms include:
- Shortness of breath (dyspnea)
- Stridor (a high-pitched noise when breathing in and/or out)
- Trouble swallowing or painful swallowing
- Drooling
Laryngitis causes
Laryngitis is most likely to happen with upper respiratory infections, especially viral ones. But it can happen for many other reasons, too. Experts split the causes into infectious and noninfectious causes. Many of the infectious causes of laryngitis are also contagious, meaning you can spread them from person to person.
Infectious causes
Infectious laryngitis causes include viruses like:
- Adenoviruses
- Common cold viruses
- Influenza and parainfluenza (croup)
- Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV)
- Rubeola (measles) and rubella (German measles)
- SARS-CoV-2 virus (COVID-19)
- Varicella (chickenpox in children and shingles in adults)
- Whooping cough (pertussis)
Bacteria that can cause infections and laryngitis include:
- Haemophilus influenzae
- Moraxella catarrhalis
- Streptococcus pneumoniae or other streptococcus species
While not as common, you can also get laryngitis from a fungal infection. This is usually from the same fungi that cause aspergillosis or candidiasis. You’re less likely to get laryngitis from a fungal infection unless your immune system is weakened or you’re taking inhaled steroids.
Noninfectious causes
Laryngitis can happen for several reasons that aren’t diseases you can catch. These include:
- Allergies
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
- Inhalation injuries (like from smoke inhalation)
- Irritation from chronic alcohol overuse, pollution, smoking and secondhand smoke
- Overuse injuries or trauma (like overusing your voice, screaming, yelling or singing)
- Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis (RRP), which usually happens because of human papillomavirus (HPV)
- Vocal cord lesions or tumors, including benign (noncancerous) growths and malignant (cancerous) tumors
Risk factors
Laryngitis can affect people of all ages. You’re more prone to this condition if you:
- Are a heavy drinker
- Are frequently exposed to tobacco smoke
- Have a respiratory infection like bronchitis or sinusitis
- Overuse your voice
Complications of laryngitis
Acute laryngitis doesn’t usually cause complications. The main exception is when you also have inflammation of a nearby structure, like epiglottitis. That can cause severe enough swelling to block off your airway. That can be life-threatening, so it’s important to get laryngitis diagnosed and treated if you have any of the dangerous symptoms.
Chronic laryngitis can have complications depending on the cause. Over time, damage from the condition can lead to scarring or other permanent changes. Your healthcare provider can tell you more about the complications that might happen with your specific case.
link